i begin this article by sharing how often organizations ask for practical clarity around trustworthy artificial intelligence. Across startups, enterprises, and public institutions, many teams struggle to balance innovation with responsibility. The NIST AI Risk Management Framework 1.0 Pdf answers this exact challenge by offering a structured and voluntary approach to managing AI risks across the full lifecycle.
i have seen governance discussions collapse because teams treat AI risk as either purely technical or purely legal. This framework avoids that trap. It blends culture, process, and engineering into one cohesive model. Within the first few pages, the document establishes why trustworthiness is not a feature added at the end but a design principle embedded from the start.
For readers searching for the nist ai risk management framework 1.0 pdf, the value lies beyond the download itself. The framework helps decision makers identify where AI can fail, who might be harmed, and how accountability should function before deployment. It also respects real world constraints by remaining sector agnostic and nonbinding.
i approach this topic as someone who has evaluated AI governance models across healthcare, automation, and generative systems. What stands out is how clearly NIST frames risk as a continuous process rather than a checklist. This article walks through the structure, functions, and practical uses of the framework so readers can confidently apply it in real environments.
Read: LangChain-OpenAI: The Backbone of Production AI Systems
What Is the NIST AI Risk Management Framework 1.0



The NIST AI Risk Management Framework 1.0 is a voluntary guidance document released in 2023 by National Institute of Standards and Technology. It helps organizations manage risks associated with artificial intelligence systems while promoting trustworthy development and use.
The framework defines AI risk as the potential for negative impacts on individuals, organizations, and society. Rather than focusing only on compliance, it emphasizes outcomes such as safety, fairness, transparency, and accountability. This approach makes it flexible enough for both startups and regulated industries.
One of its strongest design choices is lifecycle coverage. Risk considerations apply from conception and data collection through deployment and ongoing monitoring. The framework recognizes that AI systems evolve over time, especially when models retrain or interact with new environments.
By remaining technology neutral, the document avoids locking guidance to a single model type. This allows it to apply equally to classical machine learning systems and emerging generative models.
Trustworthy AI Characteristics Defined



The framework outlines six core trustworthiness characteristics that guide every decision. These characteristics shape how risks are identified and mitigated.
Valid and reliable systems behave consistently across intended contexts. Safe and secure systems resist misuse, attacks, and unexpected failures. Accountability and transparency ensure clear responsibility for outcomes. Explainability allows stakeholders to understand system behavior. Privacy enhancement protects personal and sensitive data. Fairness focuses on bias detection and mitigation.
i appreciate how these characteristics avoid vague ethics language. Each trait connects directly to measurable actions, testing protocols, and governance responsibilities. This clarity makes discussions with engineering and leadership teams far more productive.
The Four Core Functions Explained
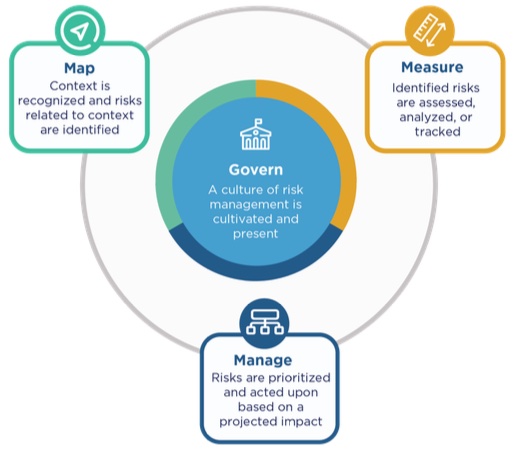
At the heart of the framework are four functions that structure risk management activities.
GOVERN establishes organizational culture, policies, and accountability structures. MAP identifies system context, stakeholders, and potential harms. MEASURE evaluates risks through testing, metrics, and validation. MANAGE prioritizes and responds to risks through mitigation, monitoring, and system updates.
These functions are not linear steps. i often describe them as a loop where insights from deployment feed back into governance decisions. This dynamic design reflects how AI behaves in real operational settings.
GOVERN Building Responsible AI Culture


GOVERN focuses on leadership commitment, documented policies, and clear ownership. Without this foundation, technical controls fail to scale.
i have seen teams underestimate how much culture shapes AI outcomes. The framework pushes senior leadership involvement rather than delegating ethics entirely to engineers. Risk tolerance, escalation paths, and documentation practices all live within this function.
It also addresses third party risks. Vendors, pretrained models, and external data sources must align with organizational values and risk thresholds.
MAP Understanding Context and Impact


MAP ensures teams understand where and how AI operates. This includes intended users, affected populations, and environmental conditions.
Contextual awareness prevents misuse and scope creep. A model built for decision support can become harmful if repurposed for automation without safeguards. The framework encourages explicit documentation of assumptions and limitations.
This function often surfaces ethical risks early, saving time and cost later.
MEASURE Testing and Evaluating Risk

MEASURE translates abstract risks into observable signals. Metrics, benchmarks, and testing protocols assess accuracy, bias, robustness, and security.
i value how the framework avoids prescribing specific tools. Instead, it encourages organizations to select methods appropriate to their domain. This flexibility supports innovation while maintaining accountability.
Continuous measurement acknowledges that AI performance drifts over time, especially in dynamic environments.
MANAGE Mitigation and Continuous Oversight


MANAGE turns insight into action. Teams prioritize risks, apply controls, and monitor outcomes. Decommissioning is also addressed, an often ignored but critical step.
Risk management does not end at deployment. The framework stresses ongoing review, incident response, and system updates. This mirrors how mature security programs operate.
Practical Implementation Checklist
| Function | Key Focus | Practical Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| GOVERN | Leadership and policy | Clear accountability |
| MAP | Context and stakeholders | Reduced misuse |
| MEASURE | Metrics and testing | Evidence based decisions |
| MANAGE | Mitigation and monitoring | Sustained trust |
This table reflects how organizations often operationalize the framework in stages.
Who Should Use This Framework

The framework applies across sectors including healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and education. Startups benefit by embedding trust early, while large organizations gain consistency across teams.
i often recommend it to teams preparing for international markets. Even though voluntary, it aligns well with emerging global standards.
Key Takeaways
- AI risk is organizational, not just technical
- Trustworthiness must be designed, not assumed
- Continuous monitoring matters more than one time audits
- Leadership involvement shapes outcomes
- Flexibility allows cross industry adoption
Conclusion
i conclude by emphasizing that the NIST AI Risk Management Framework 1.0 is not about slowing innovation. It provides structure for building AI systems people can trust. By focusing on governance, context, measurement, and action, organizations gain clarity instead of fear.
The real power of the framework lies in its adaptability. Teams can scale practices as systems grow more complex. As AI becomes more embedded in daily life, this approach helps ensure technology serves human values rather than undermining them.
For anyone evaluating AI governance seriously, this framework offers a practical and thoughtful foundation.
Read: The Limits of Current AI Model Intelligence
FAQs
Is the NIST AI RMF 1.0 mandatory
No. It is voluntary and nonregulatory, designed to guide rather than enforce.
Does it apply to generative AI
Yes. Although technology neutral, its principles apply to generative systems.
Who published the framework
It was published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
Can small startups use it
Yes. It scales well for small teams and early stage products.
Does it replace legal compliance
No. It complements existing laws and regulations.



